The Best Pharmaceutical Coating Techniques for 2026
In the rapidly evolving world of pharmaceutical coating, experts are keen on the innovative techniques for 2026. Dr. Emily Hartman, a leading authority in the field, emphasizes, “Effective pharmaceutical coating is vital for enhancing drug delivery and patient compliance.” Her insight highlights the growing importance of technology in this sector.
As pharmaceutical companies strive for better solutions, many face challenges in achieving optimal coating results. Every technique has its strengths and weaknesses. The quest for the perfect coating often leads to unexpected hurdles. Issues like film thickness and dissolution rates can complicate the process.
Furthermore, the need for customization in coatings cannot be ignored. Each medication demands a tailored approach, yet this adds complexity to the manufacturing process. Balancing efficacy with production efficiency remains a constant battle. As we look forward to 2026, the industry must continue to question and refine its methods for progress in pharmaceutical coating.

Future Trends in Pharmaceutical Coating Techniques for 2026

In 2026, the pharmaceutical coating landscape is expected to evolve significantly. A recent study predicts that the global pharmaceutical coating market will reach approximately $16.4 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of about 7.3%. This surge highlights the importance of innovative coating techniques that enhance drug delivery and efficacy.
Coating technologies like enteric, sustained-release, and controlled-release are gaining traction. Enteric coatings protect drugs from stomach acid, ensuring they reach the intestines. Controlled-release coatings improve patient compliance by minimizing dosing frequency. These techniques are not just trendy; they address the pressing need for personalized medicine, enabling tailored therapeutic outcomes.
**Tip:** Focus on emerging formulations. They can lead to better stability and bioavailability of drugs, enhancing treatment effectiveness.
While these advancements are promising, challenges remain. The complexity of materials and processes calls for rigorous testing. Manufacturers must ensure safety and consistency in production. Quality control measures need to evolve as well, to adapt to these new technologies.
**Tip:** Regularly evaluate the processes. Continuous improvement is essential in a rapidly evolving market.
Innovative Technologies Revolutionizing Coating Processes
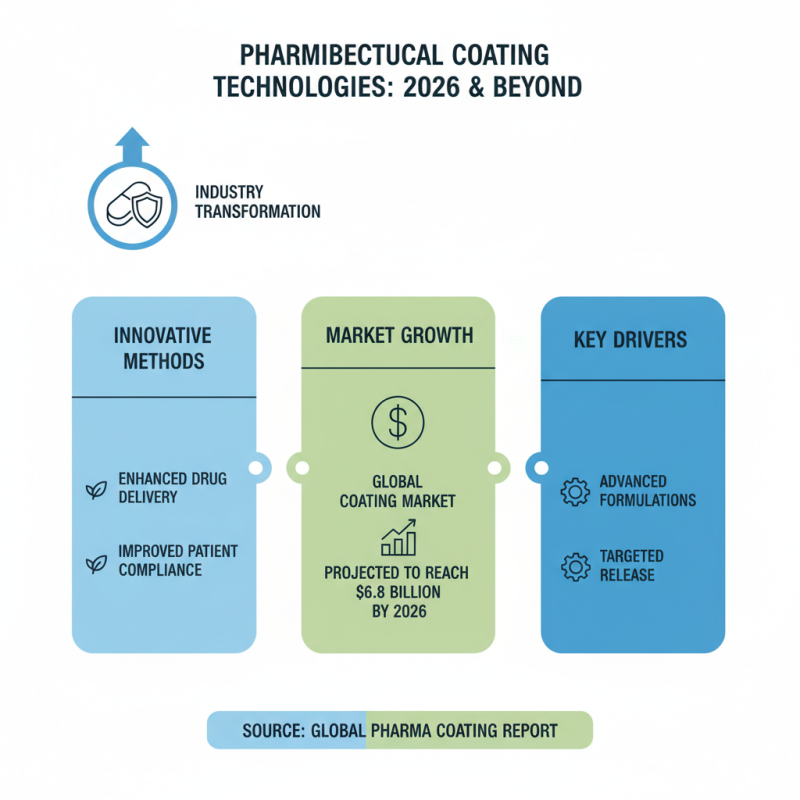
In 2026, pharmaceutical coating technologies are set to transform the industry significantly. Innovative methods are emerging that enhance drug delivery and improve patient compliance. Data from the Global Pharma Coating Report suggests that the market for pharmaceutical coatings is projected to reach $6.8 billion by 2026, driven by these advancements.
One of the notable trends is the integration of nanotechnology in coatings. This technique allows for the creation of thinner, more efficient layers that can improve the release profiles of medications. Studies have shown that nanoparticles can enhance bioavailability, achieving up to 80% improvement in some formulations. Yet, the use of such technologies raises concerns. Not every coating system can guarantee uniformity, potentially affecting dosage accuracy.
Another exciting development is the application of smart coatings. These materials can respond to environmental stimuli, releasing drugs when specific conditions are met. While promising, this technology also faces challenges related to manufacturing scalability. Many facilities struggle to incorporate smart technologies into existing processes. A recent industry survey indicated that over 40% of companies are exploring solutions but find integration complex and costly.
Comparative Analysis of Coating Materials and Their Applications
In the evolving landscape of pharmaceutical coatings, selecting the right materials is crucial. Various coating techniques are available, each with unique advantages and drawbacks. For instance, enteric coatings often utilize polymers like cellulose acetate phthalate. These materials protect drugs from gastric conditions, ensuring effective release in the intestines. However, challenges may arise in scaling production processes.
Moreover, sustained-release coatings are becoming pivotal in drug delivery. Formulations often use ethylcellulose, providing prolonged action. A report from the International Journal of Pharmaceutics suggests that 72% of drug developers are prioritizing sustained-release profiles in their products. Yet, achieving an optimal release rate remains a complex task. The balance between viscosity and coating thickness needs careful adjustment.
Natural polymers are gaining traction too. They offer biocompatibility and reduced toxicity. However, sourcing and consistency can be an issue. A study highlighted that 65% of formulators face challenges in sourcing uniform raw materials. Using natural coatings often requires extensive optimization, which may delay timelines. As the industry pushes towards innovative materials, these factors warrant attention.
Regulatory Standards Impacting Pharmaceutical Coating Methods
When it comes to pharmaceutical coating methods, regulatory standards play a crucial role. In 2026, compliance with these regulations will be vital. For instance, the FDA and EMA enforce stringent guidelines on excipients and coating materials. A recent industry report highlighted that non-compliance can lead to up to a 30% increase in rejection rates.
In terms of technical details, modern coatings often use polymers, lipids, and other materials. Their effectiveness can be hampered by improper selection. Many manufacturers fail to account for solubility issues. This oversight can lead to inconsistent drug release profiles. As a result, regulatory hurdles may arise, impacting market access.
Tips: Always validate your coating materials with current regulatory standards. Periodically review industry guidelines to avoid costly mistakes. Being proactive about compliance can streamline your production process. Regular audits and updates will improve your reliability and efficiency.
The Best Pharmaceutical Coating Techniques for 2026 - Regulatory Standards Impacting Pharmaceutical Coating Methods
| Coating Technique | Description | Regulatory Standards | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enteric Coating | Protects the drug from being released in the stomach, allowing it to dissolve in the intestines. | FDA 21 CFR Part 211 | Oral medications for sensitive compounds |
| Sugar Coating | Enhances taste masking and protects tablets from moisture. | USP <420> Sugar Coating | Pediatric formulations |
| Film Coating | Provides a thin film barrier that prevents degradation and improves handling. | FDA 21 CFR Part 210 | Solid oral dosage forms |
| Sustained Release Coating | Controls the rate of drug release over time, enhancing therapeutic efficacy. | ICH Q8(R2) | Chronic condition management |
| Enteric Film Coating | A type of film coating that is resistant to gastric fluids but soluble in intestinal fluids. | FDA Guidance for Industry | Targeted delivery to intestinal tract |
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Advanced Coating Techniques
The pharmaceutical industry is evolving rapidly. Advanced coating techniques promise increased efficacy and safety. However, implementing these techniques comes with notable challenges.
One of the main obstacles is material compatibility. Each formulation requires specific coatings. Misalignment can lead to failures, such as inconsistent drug release. Testing various combinations can be time-consuming and costly. Material restrictions often cause frustration, as not all coatings are suitable for all drugs.
Another significant challenge is the scalability of new technologies. Laboratory successes do not always translate to large-scale production. Transitioning from smaller batches to mass production often reveals unforeseen issues. Equipment limitations can hinder progress, and operational costs may soar unexpectedly. Companies need to establish robust processes to streamline this transition, while also maintaining quality.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using a Tablet Coating Pan for Efficient Coating Process
-
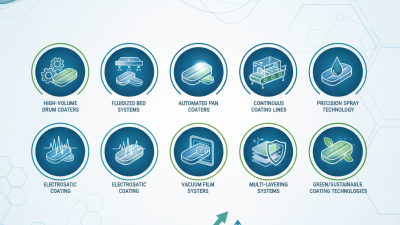
Top 10 Tablet Coating Systems for Improved Pharmaceutical Production Efficiency
-

Why Coating Pan Tablets are Essential for Efficient Tablet Production
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Pharma Coating Machine for Your Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Film Coating for Your Projects and Applications
-
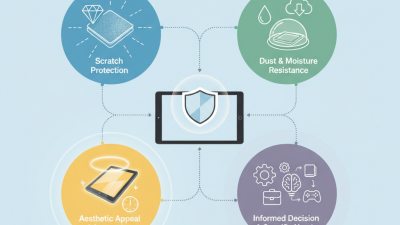
How to Choose the Best Tablet Coating for Optimal Protection and Longevity
