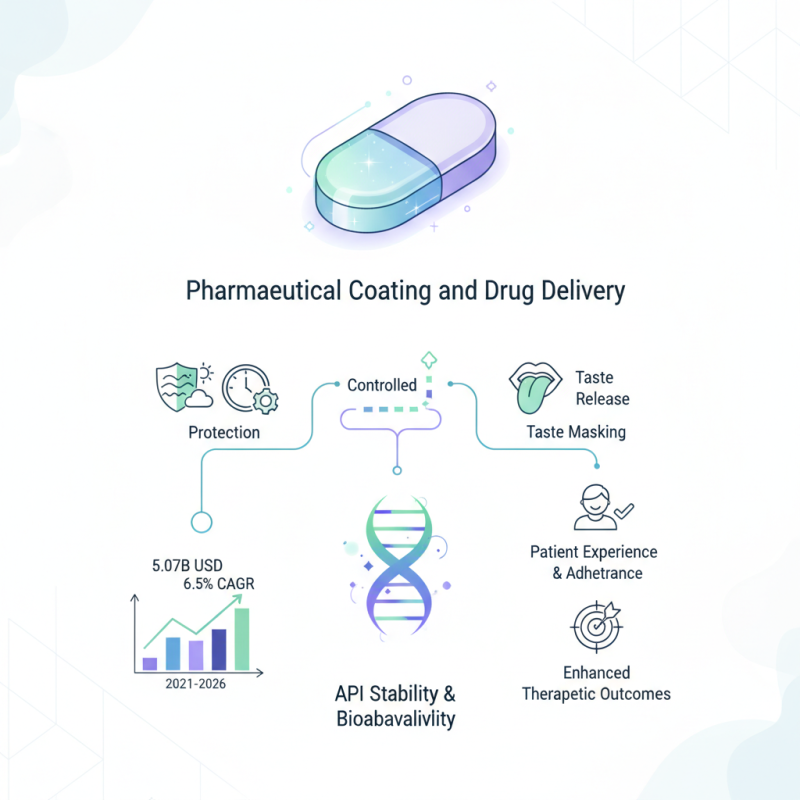
What is Pharmaceutical Coating and How Does It Impact Drug Delivery
Pharmaceutical coating plays a crucial role in the drug delivery system, influencing not only the stability and bioavailability of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) but also the overall patient experience. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pharmaceutical coating market is projected to grow from USD 5.07 billion in 2021 to USD 6.93 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%. This growth underscores the increasing importance of coatings in the pharmaceutical industry, as they aid in protecting drugs from environmental factors, controlling the release of the API, and masking unpleasant tastes.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in pharmaceutical technology, emphasizes the transformative power of pharmaceutical coatings by stating, “The right coating can significantly enhance drug absorption and ensure that therapeutic effects are delivered precisely as intended.” With advancements in coating technologies, such as enteric and sustained-release coatings, the potential for improved therapeutic outcomes is substantial. The enhanced performance of coated formulations not only boosts efficacy but also contributes to patient adherence, a critical factor in the overall success of pharmacotherapy.
As the complexity of drug formulations continues to increase, the role of pharmaceutical coating is set to become even more central to drug development. Understanding the mechanisms and benefits of these coatings is essential for researchers and manufacturers striving to innovate and improve drug delivery systems in an ever-evolving market.
Definition and Purpose of Pharmaceutical Coating
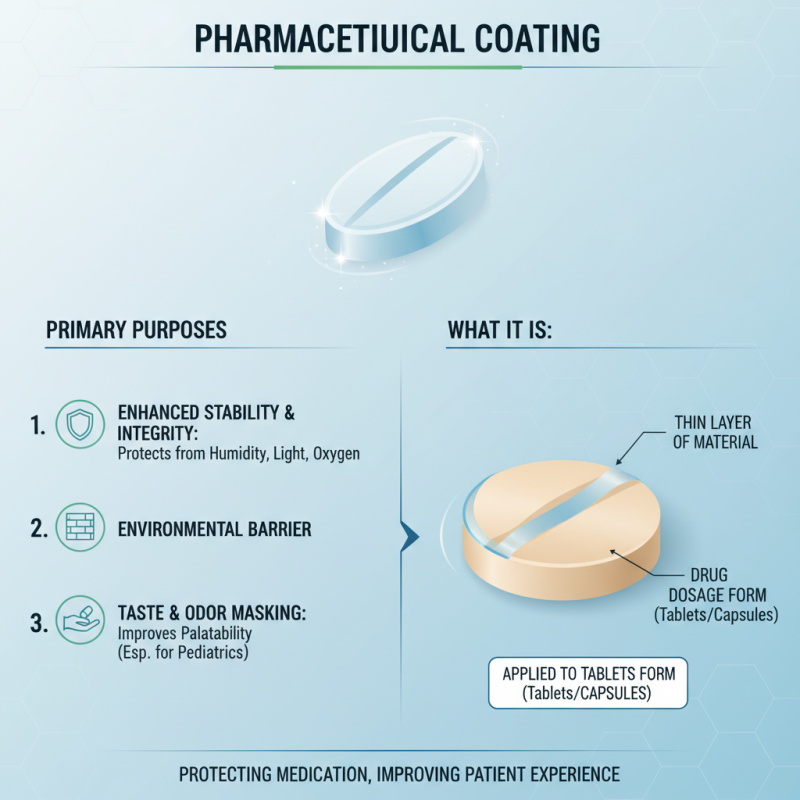
Pharmaceutical coating refers to the application of a thin layer of material onto the surface of a drug dosage form, such as tablets or capsules. The primary purpose of this coating is to enhance the stability and integrity of the medication, protecting it from environmental factors such as humidity, light, and oxygen. Additionally, coatings can serve as a barrier to mask any unpleasant taste or odor, making the medication more palatable for patients, particularly in pediatrics.
Beyond protection and taste-masking, pharmaceutical coatings play a critical role in drug delivery. Different types of coatings can control the release rate of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in the body. For instance, enteric coatings prevent the disintegration of the tablet in the stomach, allowing it to reach the intestine where the drug can be absorbed more effectively. This targeted release not only maximizes therapeutic efficacy but also minimizes side effects, leading to improved patient compliance. Overall, pharmaceutical coating is a vital technological innovation that significantly impacts the effectiveness and safety of drug delivery systems.
Types of Pharmaceutical Coatings Used in Drug Delivery
Pharmaceutical coatings are crucial in enhancing drug delivery, offering various types that cater to specific therapeutic needs. One of the most common types is enteric coating, which protects drugs from the acidic environment of the stomach, allowing them to dissolve in the more alkaline environment of the intestines. This is particularly useful for drugs that could be destabilized by stomach acid or those that are intended to have targeted effects in the intestinal tract.
Another widely used type is sustained-release or controlled-release coatings. These coatings regulate the release of the drug over an extended period, improving the overall efficacy and reducing the frequency of dosing. This technology not only improves patient compliance but also maintains consistent therapeutic levels of medication in the bloodstream, enhancing treatment outcomes for chronic conditions.
Tips: When considering drug formulations, pay attention to the specific coating used, as it can significantly influence the drug's absorption and effectiveness. Moreover, understanding the characteristics of different coatings can help healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding medication schedules for optimal patient care. Lastly, for patients, always consult with your healthcare professional regarding the best practices for taking coated medications to ensure maximum benefit.
Impact of Pharmaceutical Coating on Drug Delivery
This chart illustrates the efficiency of different types of pharmaceutical coatings on drug delivery. Higher percentages indicate greater efficacy in delivering the drug to its intended site in the body.
Mechanisms of Coating Impact on Drug Release Profiles
Pharmaceutical coating plays a crucial role in drug delivery systems by influencing the release profiles of active ingredients. The initial mechanism of coating involves creating a barrier that protects the drug from environmental factors like moisture and light, which can degrade its efficacy. Furthermore, coatings can be designed to dissolve at specific pH levels, allowing for targeted drug release in various sections of the gastrointestinal tract. This targeted approach not only enhances the bioavailability of the drug but also minimizes side effects by ensuring that the active ingredient is released only where it is most effective.
Another significant aspect of pharmaceutical coatings is the controlled release mechanism, which can be achieved through various coating materials and techniques. For instance, enteric coatings can prevent premature dissolution in the acidic stomach environment, leading to release in the more neutral pH of the intestines. This tailored release profile is essential for medications that require sustained release over time, improving patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes.
Tips: When considering pharmaceutical coatings, it’s important to evaluate the solubility and stability of the drug, as well as the desired release rate. Working with a pharmaceutical scientist can facilitate the selection of the most suitable coating material and technique, ensuring optimal drug delivery and efficacy. Additionally, understanding the physicochemical properties of both the drug and the coating can greatly influence the success of the formulation.
Advantages and Challenges of Pharmaceutical Coating Techniques
Pharmaceutical coating is a critical process that enhances drug delivery systems, providing various advantages while also presenting unique challenges. One significant advantage of coating techniques, such as enteric and sustained-release coatings, is their ability to protect sensitive drug compounds from the harsh gastrointestinal environment, thus improving the bioavailability of the drug. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global drug delivery coatings market is expected to reach approximately USD 8.5 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for orally administered pharmaceutical products. Coatings can also facilitate the controlled release of drugs, ensuring that therapeutic levels are maintained over extended periods while minimizing side effects associated with peak concentrations.
Despite these benefits, the implementation of pharmaceutical coatings does come with challenges. One notable issue is the consistency and reproducibility of coating processes. Variations in coating thickness can lead to uneven drug release profiles, posing difficulties in achieving desired therapeutic outcomes. A study published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutics found that nearly 25% of formulated products may not meet quality specifications due to coating irregularities. Additionally, there is a need for extensive research and development to refine coating materials and techniques, as well as to ensure regulatory compliance. As the industry pushes towards more personalized medicine, addressing these challenges will be paramount in harnessing the full potential of pharmaceutical coatings and enhancing patient outcomes.
Future Trends in Pharmaceutical Coating Technologies
The pharmaceutical coating industry is witnessing significant advancements that are reshaping drug delivery methods. One of the most prominent trends is the increased use of targeted coating technologies that enhance the precision of drug release. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global pharmaceutical coatings market is expected to reach USD 4.83 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%. This growth is largely driven by the demand for novel drug delivery systems that minimize side effects and improve therapeutic efficacy.
Another emerging trend is the integration of nanotechnology in pharmaceutical coatings. Nanocoatings enable improved bioavailability and controlled release profiles, which are essential for drugs with narrow therapeutic windows. A study published in the Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology highlighted that nanoparticles can enhance the solubility and stability of poorly water-soluble drugs, thus broadening the range of treatable conditions. As regulatory bodies become more accommodating toward innovative delivery techniques, the incorporation of such advanced materials into coating formulations is expected to proliferate, ultimately transforming patient care paradigms.
Moreover, advances in smart coating technologies—such as stimuli-responsive systems—are revolutionizing how pharmaceuticals are delivered. These coatings can respond to specific biochemical signals, releasing the drug only when conditions are right, such as changes in pH or temperature. The potential of such systems is backed by market insights indicating that smart drug delivery technologies could capture a significant share of the pharmaceutical market by 2030. As the focus shifts toward personalized medicine, the role of pharmaceutical coatings will remain pivotal in optimizing drug delivery and improving patient outcomes.
What is Pharmaceutical Coating and How Does It Impact Drug Delivery - Future Trends in Pharmaceutical Coating Technologies
| Coating Type | Functionality | Impact on Drug Delivery | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Film Coating | Protects the tablet core and masks taste | Improves patient compliance through palatable formulations | Development of sustained-release coatings |
| Enteric Coating | Prevents dissolution in the stomach | Targeted delivery to the intestine for improved absorption | Innovations in polysaccharide coatings |
| Sustained Release Coating | Controls the release rate of the drug | Reduces frequency of dosing | Smart polymers for on-demand release |
| Controlled Release Coating | Provides a predictable drug release profile | Improves therapeutic effects | Nanoparticle-based delivery systems |
| Functional Coatings | Includes bioadhesive properties | Enhances retention in specific areas of the gastrointestinal tract | Integration with targeted therapies |